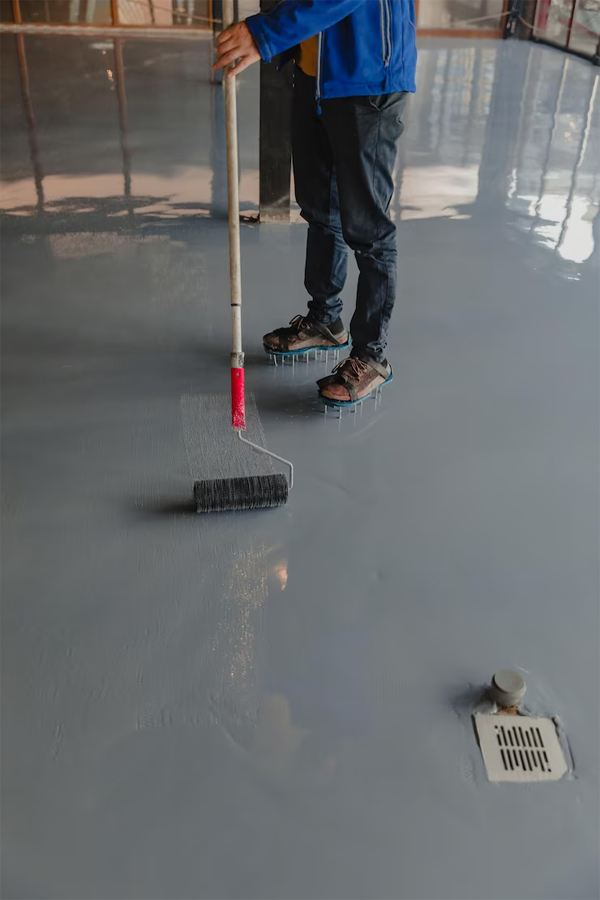
Floor coatings are protective layers applied to flooring surfaces to enhance durability, appearance, and performance. They are commonly used in industrial, commercial, and residential settings. Here’s a quick breakdown:
Epoxy Coatings – Durable, chemical-resistant, ideal for warehouses, garages.
Polyurethane Coatings – More flexible than epoxy; resists UV light.
Polyaspartic Coatings – Fast-drying and UV-stable; often used for decorative finishes.
Acrylic Coatings – Quick application and drying, used more in light-duty areas.
Cementitious Urethane – Very tough, heat- and chemical-resistant, used in food production or wet areas.
Ucrete flooring is a type of high-performance polyurethane concrete flooring system known for its exceptional durability, chemical resistance, and hygiene.
It is widely used in industries where floors are subjected to extreme conditions, such as:

Protective coatings are materials applied to surfaces—typically metal, concrete, or plastic—to shield them from environmental or operational damage such as corrosion, abrasion, chemical exposure, or UV degradation. These coatings help extend the lifespan and maintain the performance of structures, equipment, and products.


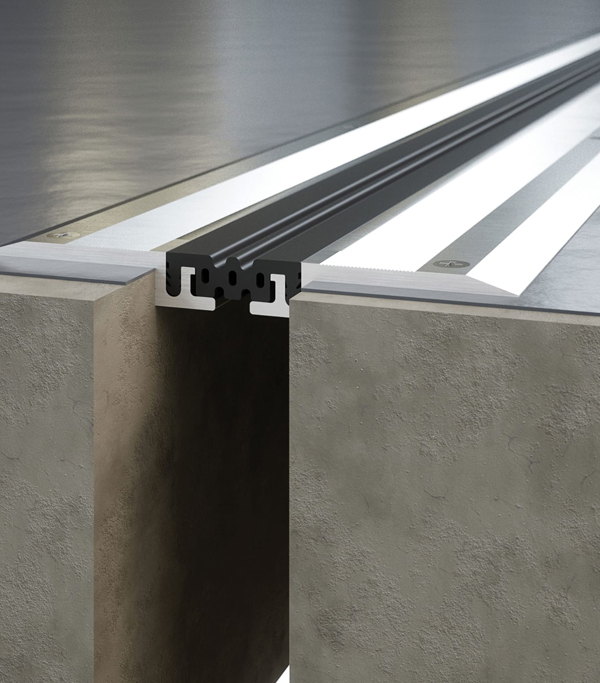
Expansion joints are specially designed gaps or spaces incorporated into structures, pipelines, or flooring to absorb movement caused by thermal expansion and contraction, vibrations, or other forces. They allow the material or structure to safely expand or contract without causing damage like cracking, warping, or buckling.
Structural Expansion Joints Used in buildings and bridges to allow movement between sections.
Floor Expansion Joints Installed in large concrete floors or industrial flooring to control cracking.
Pipe Expansion Joints Flexible joints that absorb movement in piping systems.
Metal or Rubber Expansion Joints Flexible seals that accommodate movement and vibration in ducts or pipelines.
